by Duncan Crosthwaite | Jan 20, 2025
Energy storage is a hot topic these days, especially in Scotland where the push for renewable energy is stronger than ever. But let’s face it, the world of energy storage can be a bit intimidating. There’s a lot to consider: What kind of storage system do you need? What’s the best choice for your home or business?
Whether you’re a homeowner looking to reduce your carbon footprint or a business owner aiming to make your operations more sustainable, this guide will provide the insights you need to make an informed decision.
What is a battery storage system, in a renewable energy setting?
To put it simply, a battery storage system is a device that allows renewable technologies (like Solar PV or wind turbines, to name but a few) to store the energy they create, so that it can be used at a time that’s most useful.
Without a battery storage system, the energy that’s generated would have to be used right away, whether it was needed or not.
Customers who are looking to integrate battery storage into their Solar PV system, will find they unlock a number of benefits, like uninterrupted power supply, increased independence from the grid, and lower energy bills. You can find out more about the benefits of battery storage and Solar PV in our dedicated blog.
How to Choose the Best Battery Storage System
There are several types of battery storage systems available, and choosing the right one for your needs can be a complex task. The most popular battery storage technologies include:
- Lithium-ion batteries: Currently the most common and widely used battery storage technology, lithium-ion batteries boast a high energy density, long cycle life, and operate very efficiently. They are well-suited to residential and commercial installations due to their compact size, lightweight structure, and low maintenance requirements.
- Lead acid batteries: A tried-and-tested technology, lead-acid batteries provide cost-effective energy storage solutions. However, they have a lower energy density, shorter cycle life, and require regular maintenance compared to lithium-ion batteries – which makes them a less popular choice with consumers.
- Flow batteries: Flow batteries employ a unique, liquid-based energy storage method, that makes them a scalable and long-lasting energy storage option. Although typically associated with larger installations, flow batteries are increasingly being explored for residential uses.
When choosing a battery storage technology, consider factors such as space, maintenance requirements, efficiency, and budget to ensure an ideal fit for your home or business in Scotland.
Understanding the lingo
When choosing the right battery storage solution for you, you might hear a number of terms mentioned. The ones to pay attention to, are listed below:
- Capacity: The capacity, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), signifies the amount of energy that can be stored in the battery. You need to make sure that your chosen battery storage system has sufficient capacity to cater to your energy needs during times when solar generation is low. The best way to figure this out – is to speak to an expert – like the Ceiba Renewables team.
- Depth of Discharge (DoD): DoD refers to the percentage of the battery’s total capacity that can be discharged before it requires recharging. Higher DoD values allow you to use more of the stored energy, increasing your battery’s effectiveness and extending its lifespan. A rough rule of thumb is, the higher the DoD, the better.
- Round-trip efficiency: Assess the battery’s round-trip efficiency, which indicates the percentage of energy retained during the charge and discharge process. Higher efficiency values result in more stored energy available for use.
As well as assessing a battery’s performance against each of these metrics, you also need to find one that works for your budget. Remember that as well as the cost of the battery system, you’ll also have installation, permit, and warranty costs. When speaking to customers we often calculate the cost per kilowatt-hour (kWh) for each system, which gives customers an idea of the savings available, against the cost for implementing each system. With our help, we’ll find the right one to suit your needs, that’s financially manageable for you too.
Batter storage systems really are the key to making the most of your renewable technology. And if you’re considering Solar PV – battery storage will give you higher cost savings and better energy use. We’re here to help you navigate the complexities of battery storage systems in Scotland, ensuring seamless integration into your renewable energy setup. Get in touch with Ceiba Renewables today to learn more about our battery storage solutions – it all starts with a conversation, one that we’re more than happy to have.
by Duncan Crosthwaite | Oct 18, 2024
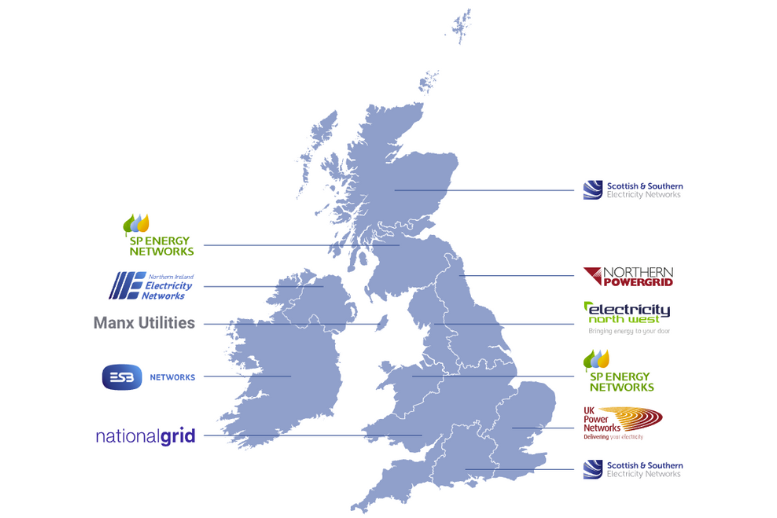
When installing a Tesla Powerwall 3 alongside a solar PV system, working with your local Distribution Network Operator (DNO) is essential. The DNO ensures your system complies with grid regulations, which can influence your battery settings and export limits. In Scotland, for example, the DNOs are SSE and Scottish Power. Below is an easy-to-follow guide on how DNO regulations like G98 and G99 may affect your installation.
What is the G98 Regulation?
The G98 regulation allows you to connect systems with an output of up to 3.68kW (equal to 16 amps) to the grid without prior approval or fees. This limit applies to both your solar panels and battery system combined, making it a simple and cost-effective option for smaller installations, combatting climate change.
Why Does the G99 Regulation Matter?
If your solar panels and battery system together exceed 3.68kW, you’ll fall under the more complex G99 regulation. Even if your Tesla Powerwall 3 doesn’t export energy to the grid, the DNO considers it part of your generation system. For instance, if you have both a solar PV array and an AC-coupled battery system, the combined power could push you into G99 territory, requiring approval.
Power During an Outage: The Role of “Islanding”
One key feature of the Tesla Powerwall 3 is its ability to keep your home powered during an outage, known as “islanding.” However, if your Powerwall is capable of islanding, your system automatically requires a G99 application, even if your system doesn’t exceed the 3.68kW limit.
How G99 Applications Work
A G99 application is required for any system that outputs more than 3.68kW per phase to the grid. Note that this applies to the continuous output from your battery (on the AC side), not the capacity of your solar panels or battery storage. The DNO can take up to 45 working days (around 3 months) to process your G99 application and provide an Offer Letter, detailing any associated costs. Sometimes, there are no fees, but additional costs such as admin fees, testing fees, or even network upgrades may be required.
DNOs interpret regulations differently, meaning costs can vary widely. Some applications are approved without any fees, while others may involve significant costs. This makes it difficult to predict the exact charges in advance. Thankfully, experienced installers like Ceiba Renewables often have good relationships with DNOs, which can help streamline the process and reduce costs, especially for witness testing.
What If G99 Costs Are Too High?
If the G99 Offer Letter is too expensive, there’s an alternative: designing the system with Export Limitation. This limits the output of your solar PV and Powerwall to 3.68kW each, which can sometimes avoid the G99 fees altogether.
The G99 Fast-Track Process
Some DNOs offer a G99 Fast-Track option for systems where both the battery and solar PV are capped at 3.68kW. This fast-track process has no fees and a quicker approval time, but its availability can vary. Crucially, the Fast-Track is not available for batteries that work during power cuts.
Choose the Right Output Setting for Tesla Powerwall 3
Option 1: Apply for the Full 11.04kW Output
One approach is to apply for the total 11.04kW output and see what the DNO says. While the DNO may impose fees or require a longer approval process, applying for the maximum output ensures that you future-proof your system for potential upgrades or increased energy needs. If approved, you can take full advantage of your Powerwall 3’s capabilities and maximize energy storage and output, especially in scenarios like energy trading or high-load usage.
Option 2: Size the Powerwall Output Based on Your Solar PV
Another strategy is to size the Tesla Powerwall 3’s output to match your solar PV output, which could make the approval process smoother and quicker. For instance, if your solar system produces around 7kW, you might choose a 7kW output setting for the Powerwall. This aligns the battery’s output with your solar generation, preventing unnecessary energy clipping and ensuring optimal energy use.
This option can also help avoid costly fees or lengthy approval processes, as the DNO may find it easier to approve a system sized to balance with the solar generation rather than maxing out at the 11.04kW setting.
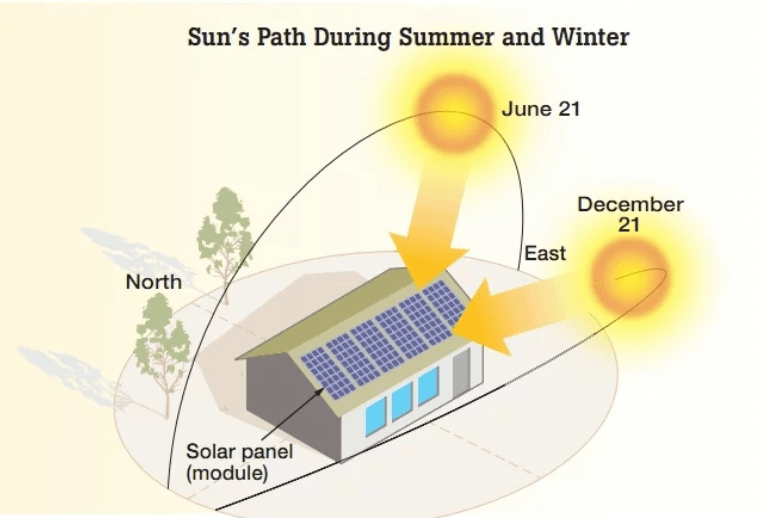
Considering Solar Panel Orientation
The orientation of your solar panels plays a key role in determining the ideal output setting. For example, if your solar panels are spread across different roof angles, the peak output might be lower than the total kWp of your system. Matching the Powerwall 3’s output to the actual power your panels are capable of generating (up to 11.04kW) ensures the system operates efficiently without overloading the grid.
Comparing Discharge and Charge Rates
With multiple output options, it’s also important to consider the impact on discharge and charge rates. For example, if your battery discharges at 11.04kW, a fully charged 13.5kWh battery will last for around 1.2 hours under heavy load (13.5kWh / 11.04kW). In contrast, a 3.68kW setting would last approximately 3.66 hours under the same conditions, offering greater endurance but slower power delivery.
Choosing the right setting depends on how you intend to use the Powerwall. If fast charging during off-peak times is a priority, higher output settings like 10kW or 11.04kW could be advantageous. However, if you’re more concerned with extending battery life during power outages, a lower setting like 3.68kW or 5kW may be more suitable.
Which Setting is Best for You?
Ultimately, the right output setting for your Tesla Powerwall 3 depends on your unique circumstances. If you have a solar system that generates 4.5kW or more, applying for the 11.04kW setting may give you the flexibility to maximize energy usage. However, if you’re concerned about DNO approval times or fees, sizing the output to your solar PV generation (for example, 6kW or 7kW) may result in faster approval and fewer complications.
As always, you can work with your installer to adjust your settings if needed, and you can even reapply with different settings based on the feedback from the DNO.
by Duncan Crosthwaite | Sep 16, 2024
At Ceiba Renewables, we’re excited to introduce the Tesla Powerwall 3 — a next-generation battery that not only eliminates rare earth metals but offers remarkable flexibility with its programmable inverter. This feature helps us navigate the unknowns of the G99 application process required by the Distribution Network Operator (DNO) when installing Powerwalls, ensuring your home can safely integrate with your home and disconnect from the grid during outages.
The Powerwall 3 charges at 5kW but can output up to 11.04kW to power your home from solar energy or export to the grid (subject to DNO approval). These capabilities optimise energy use, reduce grid dependency, and offer savings.
In this post, we’ll break down key design considerations to help you understand how the Powerwall’s settings work together to maximise your system’s efficiency.
Key Tesla Powerwall 3 Components
Solar PV kWp Rating
The kilowatt-peak (kWp) rating measures your solar panels’ maximum output under optimal conditions. A 6kWp solar system, for example, can produce up to 6kW in peak sunlight, helping meet your household power needs and storing excess energy.
G99 Setting: Battery Output to the House
The G99 setting determines how much power the Powerwall can send to your home & the grid. The Powerwall 3 can supply up to 11.04kW, but this will require approval from your DNO. Once the DNO have assessed the application, the output might need to be limited to 3.68kW, 5kW, 6kW, 7, 8, 9, 10 or 11.04kW to comply with DNO requirements.
G100 Export Limit Setting
The G100 limit governs how much excess energy can be exported back to the grid. Depending on local grid rules, this limit may be set at 3.68kW but could go as high as 11.04kW with DNO approval. Any solar energy produced beyond this limit is “clipped,” meaning it’s neither used nor exported.
Battery Charge Rate
The Powerwall 3 charges at a rate of 5kW, allowing it to efficiently store energy from solar panels or the grid for later use.
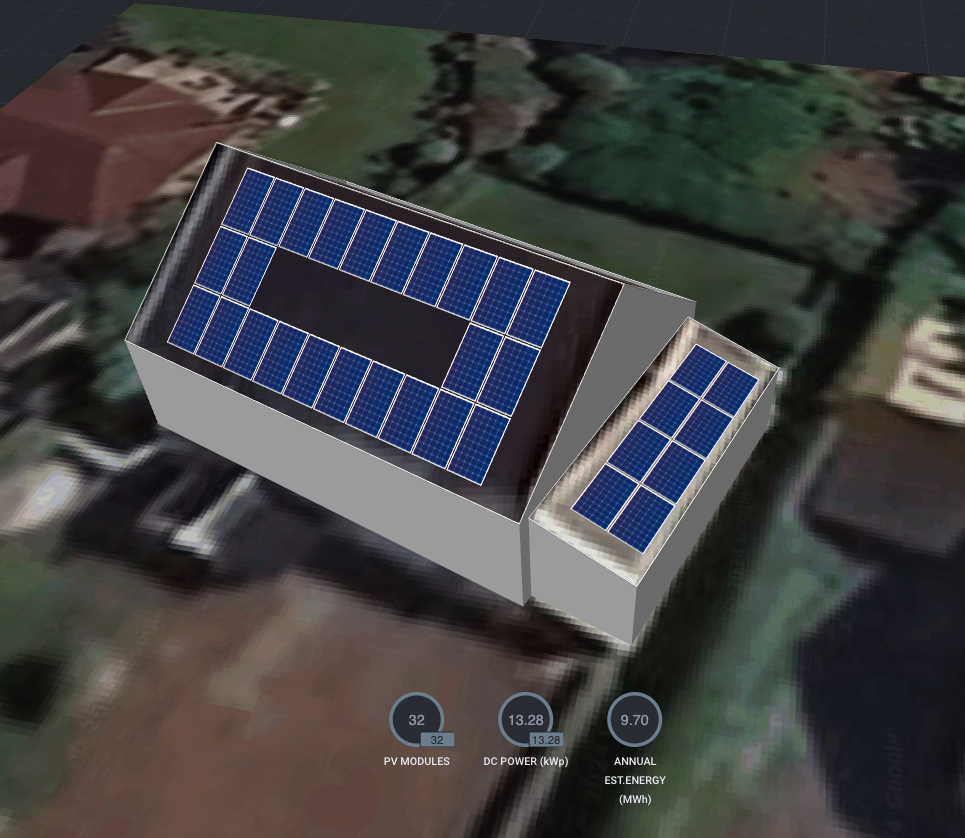
Real-World Example: Gerry’s Setup
Let’s take Gerry as an example:
- Solar PV Setup: 13.2kWp solar panels (10kW West-facing, 3.2kW South-facing).
- Powerwall 3: Storing excess solar energy.
- G100 Export Limit: 3.68kW.
Image: Gerry’s Solar System
On a sunny day, his panels might produce up to 13kW. The Powerwall charges at 5kW, leaving 8kW for household use or export. If Gerry’s home only uses 1kW at the time, 7kW is available for export, but due to the 3.68kW export limit, 3.32kW will be clipped.
Clipping: What It Means for Your System
Clipping happens when your system produces more solar power than can be used in the home and exported. In Gerry’s case, 3.32kW was clipped. Although this might sound like a loss, it only occurs during peak production meanwhile in lower light conditions the PV system can produce more power than a lower output system. Homeowners can also offset clipping by using excess energy for high-demand activities like charging an electric vehicle (EV). The Tesla Wall Charger and Zappi EV Chargers are ideal for this!
Future-Proofing Your Tesla Powerwall 3 Setup
To prepare for future energy needs:
- Cable Sizing: Use the right cables (e.g., 16mm² for an 11.04kW output) to handle future Powerwall upgrades.
- G99 Applications: To unlock the full 11.04kW output, you’ll need DNO approval. This process can take time and isn’t always guaranteed, but it can enhance your system’s flexibility and potential for financial returns, especially with energy trading.
When designing your Tesla Powerwall 3 system:
- Lower output settings ensure regulatory compliance but may limit energy use and exports.
- Higher solar PV ratings generate more energy but could lead to clipping during peak production.
- Your system’s settings will depend on your energy needs, local DNO requirements, and future goals.
Choosing the 11.04kW output option may require extra time for DNO approval, and we may need to resubmit applications if approval is denied.
We’ll tailor your Tesla Powerwall 3 system based on your specific needs and DNO limitations. Here’s an example of how your settings might look:
|
Setting
|
Example Value
|
|
Solar PV Rating (kWp)
|
13.2kW
|
|
Battery Output (G99)
|
11.04kW
|
|
Export Limit (G100)
|
3.68kW
|
|
Battery Charge Rate
|
5kW
|
Feel free to reach out with any questions or to learn more about optimising your Tesla Powerwall 3 system!
by Filip Rasinski | Mar 11, 2024
Investing in a renewable energy system for your home or business comes with numerous benefits, such as lower energy bills, reduced carbon footprint, and even potential income through government incentives. However, to truly maximise these benefits, it’s essential to ensure the efficiency and performance of your renewable energy system are optimised. Ceiba Renewables is committed to providing guidance and support, enabling you to make the most of your green energy investment.
In this article, we will share seven expert tips from our team, which will help you enhance the performance, efficiency, and reliability of your renewable energy system. These tips are applicable to various renewable energy technologies, such as solar panels, wind turbines, and heat pumps. By implementing these best practices, you can not only save more on your energy bills but also contribute to a more sustainable future for generations to come.
Energy Efficiency Audit: Assess Your Current Performance
The first step towards maximising your renewable energy system’s efficiency is conducting a thorough energy efficiency audit. An audit helps you identify areas in your property where energy wastage occurs and provides insight into potential improvements. By addressing these inefficiencies, you can reduce energy consumption and enhance the performance of your renewable energy system.
Some areas to consider during an energy audit include:
- Insulation: Check the insulation levels in your property’s walls, attic, and floors. Proper insulation prevents heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, reducing the demand on your heating and cooling systems.
- Ventilation: Ensure that your property has adequate ventilation, allowing for efficient air circulation, moisture control, and a healthy indoor environment.
- Appliances: Evaluate the energy efficiency of your appliances and consider upgrading to energy-saving models where possible.
- Lighting: Switch to energy-efficient LED light bulbs and make sure to turn off lights when not in use.
Optimal System Sizing and Design
A renewable energy system’s size and design play a crucial role in its overall efficiency. For instance, a solar panel system should be designed according to your property’s orientation, roof space, and energy consumption needs to ensure optimal performance.
When determining the appropriate size for your renewable energy system, make sure to consult with an expert provider. We can help you develop a tailored system that balances your power needs with the available resources, maximising both efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Regular Maintenance and Inspections
To maintain optimal performance, it’s essential to establish a routine of regular maintenance and inspections for your renewable energy system. Some best practices include:
- Clean your solar panels or wind turbine blades periodically to remove dust, dirt, and debris that may impact their performance.
- Inspect your renewable energy equipment for signs of wear or damage, and address any issues as soon as possible.
- Maintain and monitor energy storage configurations, such as battery systems, to ensure optimal functionality.
- Have your renewable energy system periodically inspected by a certified professional for thorough examinations and preventative maintenance.
Balance Your Energy Consumption Patterns
Balancing your energy consumption patterns with your renewable energy system’s production rates can help maximise efficiency and align your energy usage to the times when your system generates the most energy. For example, if you have a solar panel system, consider undertaking high-energy tasks, such as running your dishwasher or doing laundry, during periods of peak sunlight.
Additionally, implementing energy-saving habits like turning off appliances when they’re not in use and replacing old electronics with more energy-efficient alternatives can further augment the efficiency of your renewable energy system.
Opt for Energy Storage Solutions
Investing in an energy storage solution, such as a battery system, can help you store excess solar or wind-generated energy for use during periods of low energy production or higher demand. By storing this energy, you can effectively reduce your reliance on the grid and ensure that your renewable energy system provides a more consistent power supply, ultimately improving its overall efficiency.
However, it’s essential to assess the costs and benefits of adding an energy storage system to your renewable energy installation, as it may not always be the most cost-effective solution.
Keep Up with Technology Advancements
Renewable energy technology is continually evolving, with new advancements and innovations emerging regularly. Staying informed about these developments can help you identify potential enhancements for your renewable energy system. For example, solar panel technology improvements have led to higher efficiency rates and longer lifespans than in the past, making it worthwhile to consider upgrading older systems.
Utilise Monitoring and Control Solutions
Monitoring and control solutions, such as smart thermostats, apps, and energy management systems, can help you track your renewable energy system’s performance, providing valuable insights into potential efficiency improvements. By continuously monitoring your system’s energy production and consumption patterns, you can identify opportunities to enhance its performance further.
These monitoring tools often provide real-time data and alerts, allowing you to address any issues promptly and maintain consistent performance levels. Consider speaking with an expert to determine the most suitable monitoring and control options for your renewable energy system.
Unlock Your Renewable Energy System’s Full Potential with Ceiba Renewables
There is a myriad of measures you can take to enhance the efficiency and performance of your renewable energy system. These expert tips, covering everything from energy audits to monitoring technology, are designed to help you make the most of your green energy investment. By implementing these strategies, you’ll enjoy even greater energy bill savings, further reducing your carbon footprint and contributing to a more sustainable future.
Ceiba Renewables is dedicated to providing you with the guidance and support needed to navigate the world of renewable energy. We’re here to help you maximise the benefits of your green energy system and ensure it operates optimally for years to come. Get in touch with our energy specialists now!